Opioids can be highly addictive, but healthcare providers are still writing enough prescriptions for painkillers each year for every American adult to have a bottle of pills. Are opioids the only answer for people who are suffering from acute or chronic pain? There are many alternatives to opiate-based medication for pain management available, and plenty of scientific data to support their effectiveness.
Choosing an alternative to opioids for pain could be the difference between pain relief and addiction, particularly for teens or young children who are at a higher risk of addiction due to their developing brains.
This post has been updated to reveal even more scientifically proven, non-opioid alternatives for pain management.
10 Alternatives to Opioids for Pain Management
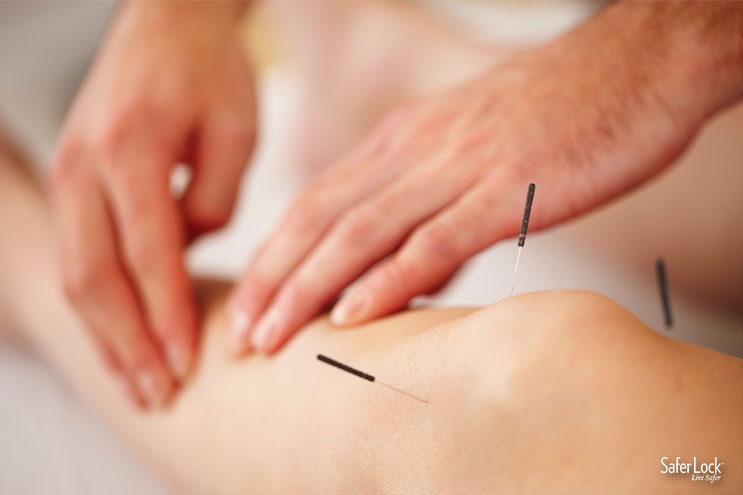
Acupuncture
Acupuncture uses needles to stimulate specific points on or under the skin. This method of treating pain, nausea, and many other conditions has been used in Eastern medicine for centuries.
How does acupuncture work?
Acupuncture needles are thought to stimulate nerves, which then:
- Send signals to the brain to release feel-good hormones such as beta-endorphins
- Reduce pro-inflammatory markers that lead to inflammation and pain
- Stimulate nerve growth factor that helps the nerve to regenerate
How effective is acupuncture?
Research has shown the effectiveness of acupuncture for many pain conditions, including
- Back or neck pain
- Osteoarthritis
- Headaches and migraines
- Myofascial pain syndrome
- Sciatica
- Postoperative pain
- Cancer pain
- Chronic prostatitis or pelvic pain syndrome
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Fibromyalgia
A 2018 meta-analysis of over 20,000 patients in 39 high-quality randomized controlled trials found that acupuncture was superior to both sham and no acupuncture for back or neck pain, osteoarthritis, headaches, and shoulder pain. The World Health Organization even has recognized 351 standardized acupoints on the human body.
“People talk about psychedelics reshaping the nervous system. Acupuncture kind of does the same thing,” said Richard Harris, a professor and chair of UC Irvine Susan Samueli Integrative Health Institute. His group conducted a series of studies on the efficacy of acupuncture among chronic pain patients. They found that acupuncture - which was not a sham - changed brain activity in terms of activating the receptors that bind opioids, which help control pain in the body.
They also found that electroacupuncture, where needles are stimulated with minor electrical currents, also affected how different areas of the brain were connected, essentially rewiring the brain’s pain network.
Guided Imagery
Guided imagery is a pain intervention that uses relaxation techniques and visualization of calming mental images to manage acute and chronic pain.
How does guided imagery work?
When you’re under stress, your body’s fight-or-flight mechanism kicks in. Cortisol and other stress hormones can ratchet up inflammation levels in your body. Mind-body practices, like guided imagery, calm the nervous sympathetic system. While in a state of deep relaxation, you visualize your body as you wish it would be. The process eases stress and lowers cortisol levels, bringing a decrease in pain perception and anxiety with it.
How effective is guided imagery? Closing your eyes and imagining your pain away? It may sound like an ineffective method of pain management, but a comprehensive study conducted in 2020 found that this relaxation and visualization technique can be effective for the management of pain in cancer patients. In a review of seven randomized controlled studies, guided imagery brought statistically significant improvements for all 287 individuals suffering from arthritis and other rheumatic diseases.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of talk therapy that helps people identify and develop skills to manage negative thoughts and behaviors. For pain management, CBT helps patients change their awareness of pain and develop better coping skills - even if their pain doesn’t change.
Currently, CBT is the prevailing psychological treatment for individuals with chronic pain conditions such as low back pain, headaches, arthritis, orofacial pain, and fibromyalgia. CBT has also been applied to pain associated with cancer and its treatment, as well as anxiety and insomnia.
How does cognitive behavioral therapy work? CBT focuses on the relationships between thoughts, behaviors, and emotions. Negative beliefs about pain can lead to maladaptive coping, exacerbation of pain, increased suffering, and greater disability. CBT teaches patients effective coping strategies and helps replace negative thought patterns with less harmful thoughts, helping patients increase adaptive behaviors, identify and correct maladaptive thoughts and beliefs, and increase self-efficacy for pain management.
How effective is cognitive behavioral therapy? Numerous meta-analyses and large, randomized controlled studies support CBT for chronic pain. One meta-analysis reviewed 21 studies and found that CBT has positive effects on pain intensity, pain-related interference, health-related quality of life, and depression.
One large, randomized controlled trial looked at the short- and long-term effects of CBT for chronic temporomandibular disorder (TMD), a condition that can cause severe pain and discomfort that can last for years in the face, jaw, neck, and shoulders. At a 12-month follow-up, CBT patients were 3x more likely to report no pain interference and twice as likely to report clinically meaningful improvement compared to the control group.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Group therapy, music therapy, and pet therapy are among some of the most commonly used complementary and alternative therapies offered by hospice care providers to provide comfort and alleviate pain and anxiety for patients with cancer and other chronic conditions. However, complementary therapy techniques can take the form of almost any physical, psychological, or nutritional therapy—or varying combinations of all three.
How do complementary and alternative therapies work? In music therapy, certified music therapists use methods such as songwriting, improvisation, lyric analysis, singing, instrument playing, and relaxation techniques to treat the needs of patients.
Pet therapy, or animal-assisted therapy, uses animals that have been trained to be obedient, calm, and comforting to provide therapeutic benefits.
Group therapy often includes many other alternative pain management techniques, such as guided imagery, CBT, focused breathing, muscle relaxation, and visualization, applied in a group session.
How effective are complementary and alternative therapy? Numerous scientific studies are proving that complementary and alternative therapies can be effective methods for managing pain and stress.
Research conducted by the American Music Therapy Association found that music interventions had statistically significant effects in decreasing pain, emotional distress from pain, anesthetic use, opioid intake, non-opioid intake, heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration rate.
A study conducted by PLOS One concluded that therapy dogs can provide a significant reduction in pain and emotional distress for chronic pain patients.
Group therapy sessions can provide all the benefits of techniques such as CBT or guided imagery but add another layer of benefits from peer support and influence. Group sessions can lessen the isolation of a chronic pain condition and expand a patient’s support network.
A study on the effects of group therapy for pain management in chronic pain patients found a significant decrease in overall pain scores following a session. Another large, randomized, controlled study evaluated the effectiveness of group CBT therapy, with one group receiving antidepressant medication and the other receiving CBT + medication. After 12 weeks, the CBT group patients reported significantly lower levels of pain and greater satisfaction with treatment compared to those who didn’t receive group CBT intervention. They also continued both groups on antidepressants for a year after the study, and the CBT group still showed significant positive effects.
Aromatherapy With all the aroma diffusers and incense packs sold online, aromatherapy might seem like a gimmick at best. However, this method has been used for pain management dating back all the way to the first century with evidence from ancient Indian, Chinese, Egyptian, Greek, and Roman civilizations. Throughout the 11th and 15th centuries, the harnessing of plant oils for medicinal treatments developed further and became commonplace.
How does aromatherapy work? When you inhale scents of essential oils, the molecules from the olfactory nerves travel directly to your brain, especially the amygdala, which regulates how you experience your emotions. Certain essential oils, like wintergreen and other mint oils, can also be used to relax your muscles and cool the skin. Similarly, research has shown lavender oils also help some people calm down and reduce inflammation, which is why they are commonly included in bath bombs and salts.
How effective is aromatherapy? According to a meta-analysis conducted in 2022, uses of aromatherapy resulted in a significant reduction in pain, especially pain labor and postoperative pain. In addition, this study also indicated that the time after inhalation, the type of oil used, and the type of pain treated are important variables that may interfere with the magnitude of the effect.
Rosa damascena (from Demask Roses) and Lavender oil were the most effective among the studied aromas.
Massage Therapy Many people seek out massage therapy for a number of reasons, including a drug-free alternative to pain management. Massage comes in two forms: relaxation and rehabilitative massage, which can help rehabilitate injuries and reduce pain.
How does massage therapy work? There are many different forms of massage techniques, but generally, all involve the stretching and kneading of soft tissues in the body and applying pressure to various pressure points to relax muscles. But massage does more than just relax muscles; research has also shown that it can also be used to treat anxiety and depression as well as other health-related quality of life issues.
How effective is massage therapy? The effectiveness of massage therapy for pain has been supported by various studies. It has been found most effective for non-specific lower back pain, both acute and chronic, but studies have also found massage to be effective for shoulder pain, headache pain, fibromyalgia, mixed chronic pain, and neck pain.
One specific type of massage, known as Osteopathic Manual Treatment (OMT), has been found to be particularly effective for musculoskeletal disorders. OMT is administered by an osteopathic physician rather than a massage professional. In a review of clinical studies, OMT was shown to provide significant reductions in lower back pain, with results lasting up to three months.
Hypnotherapy Hypnotherapy is an alternative practice where a licensed hypnotherapist uses verbal repetition and mental images to hypnotize patients into a changed state of awareness and increased relaxation that allows for improved focus and concentration.
How does hypnotherapy work? Hypnosis used for the treatment of chronic pain typically involves a hypnotic induction followed by suggestions for comfort and relaxation. Patients are often taught a cue that they can then use on their own to quickly enter a state of comfort. In this stasis, your conscious mind is quieted, and you’re able to tap into parts of your subconscious and access deeper emotions and thoughts. While hypnotized, you’re mind is more open to gentle guidance from your hypnotherapist to help you modify or replace the unconscious thoughts that are driving your current behavior.
How effective is hypnotherapy? A review of 13 controlled studies revealed that hypnosis is significantly effective for chronic pain conditions, including low-back pain, arthritis, cancer, and disability-related pain. In some cases, hypnotherapy reduces chronic pain for up to three months. In one controlled study, fibromyalgia patients who received hypnotherapy showed significant improvements in pain reduction, as well as fatigue and sleep patterns.
Chiropractic Chiropractic care uses spinal manipulation to treat neuromusculoskeletal complaints such as back pain, neck pain, migraine headaches, fibromyalgia, and joint pain.
How does chiropractic medicine work? Chiropractors use their hands or instruments to perform spinal manipulation, adjustments, and other clinical interventions to manually restore joint mobility and heal injured tissues through controlled force. A chiropractor may also use postural and exercise education, ultrasound therapy, laser therapy, ergonomic training, and health and lifestyle counseling as well.
How effective is chiropractic medicine? The American Chiropractic Association provides excerpts and summaries from recent studies that support chiropractic care as an effective treatment for chronic and acute pain, headaches, and neck pain. Though there is stigma and skepticism regarding the effectiveness of chiropractic care, recent studies have shown that it is just as effective as physical therapy.
Herbs Natural pain treatments include herbal medicines—plants that are used to treat health problems, including pain management. The seeds, berries, roots, bark, leaves, and flowers of plants have been used as medicine long before recorded history. Many modern-day pharmacological medicines are based on herbal remedies, such as aspirin (from willow bark), digoxin (from foxglove), quinine (from cinchona bark), and morphine (from the opium poppy).
How do herbal pain treatments work? Many herbs have potent properties and multiple ingredients that have a beneficial effect on the body. Some herbs and plants have been shown to decrease inflammation and have the same pain-relieving effects as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
How effective are herbal pain treatments? Different herbs have different effects on the body. According to UCF Health, the following herbal remedies can provide all-natural relief:
- Turmeric: Anti-inflammatory spice for joint and muscle pain
- Ginger: Analgesic for headaches and muscle pain
- Willow Bark: Natural pain reliever similar to aspirin
- Boswellia: Eases joint pain, used topically or orally
- Devil’s Claw: African herb for arthritis and muscle soreness
- White Willow Bark: Salicin-based relief for various discomforts
Medical Marijuana
Medical marijuana is a controversial, non-opioid alternative for pain. More and more states are passing laws allowing medical marijuana use for conditions such as pain, headaches, nausea, seizures, and Crohn’s disease.
How does medical marijuana work? Marijuana contains hundreds of chemical compounds, but Delta 9‐Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) are the active ingredients in cannabis that modulate a patient’s symptoms. THC binds to receptors in the brain to produce effects such as reducing pain or anxiety but also provides the psychoactive sensation of being “high,” which makes this a controversial treatment option.
CBD, on the other hand, does not contain THC nor produce the same psychoactive effects. It has been approved by the FDA and proven to treat two forms of epilepsy through a prescription capsule known as Epidiolex. CBD typically comes in the form of an oil that can be ingested or applied topically, but it can also be sold in extracts, as a vaporized liquid, or oil-based capsules. Food, drink, and beauty products containing CBD also have grown very popular.
How effective is medical marijuana? More than 60 peer-reviewed studies were examined by ProCon.org, seven of which focused on marijuana’s effectiveness for pain relief. Six of the seven double-blind studies associated cannabis use with lowered chronic and neuropathic pain.
According to a report by the Mayo Clinic, medical marijuana use is generally considered safe. However, different strains of marijuana contain varying amounts of THC. This can make dosing marijuana difficult. The risk of detrimental side effects is low; a study found that medical marijuana had a better safety profile when compared to opioids for long-term chronic pain.
There is no question that using opioid painkillers can lead to addiction and put your entire family at risk for prescription drug misuse, as well as accidental overdose and medicine poisoning. There are many alternative treatments to pain relief, some more controversial than others, that may be a lower risk for your family and your health. Before you fill a prescription for an opioid painkiller, make sure you know all of the risks and alternative treatments available to you.